When the Dutch wanted to expand their territories, they turned to the North Sea to create more arable land for Dutch farmers. Likewise, Singapore has reclaimed land to expand their territories. Over 95% of Egypt’s population live along the Nile River and its fertile delta, and the population (over 110 million people) continues to grow and is seeking new options. While this isn’t expanding into the sea, it is a type of land reclamation project as they environment is modified to make the desert bloom. Both of these embedded videos are helpful introductions to the political, economic, demographic, and environmental aspects of these projects in the Middle East.
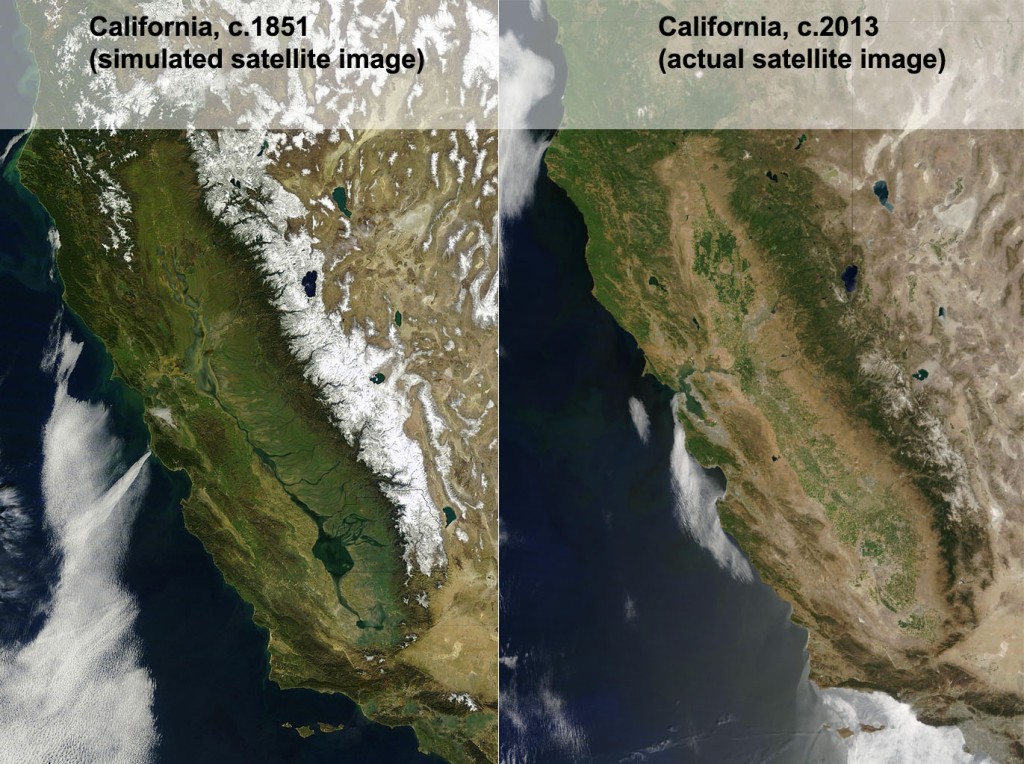
A few years ago, I was delighted to see an geographer’s rendition of what a satellite image of California would have looked if such a thing existed in the 1800s (figure 1). Back then the southern San Joaquin Valley was swampy wetland surrounding Lake Tulare, the largest freshwater lake west of the Mississippi River. In the late 1800s, canals and dams were created to divert water from the rivers that fed into the lake to go supporting agriculture and the metropolitan areas of California. As the very shallow lake dried up, the lakebed was converted into was converted to agricultural land, mainly under cotton cultivation.
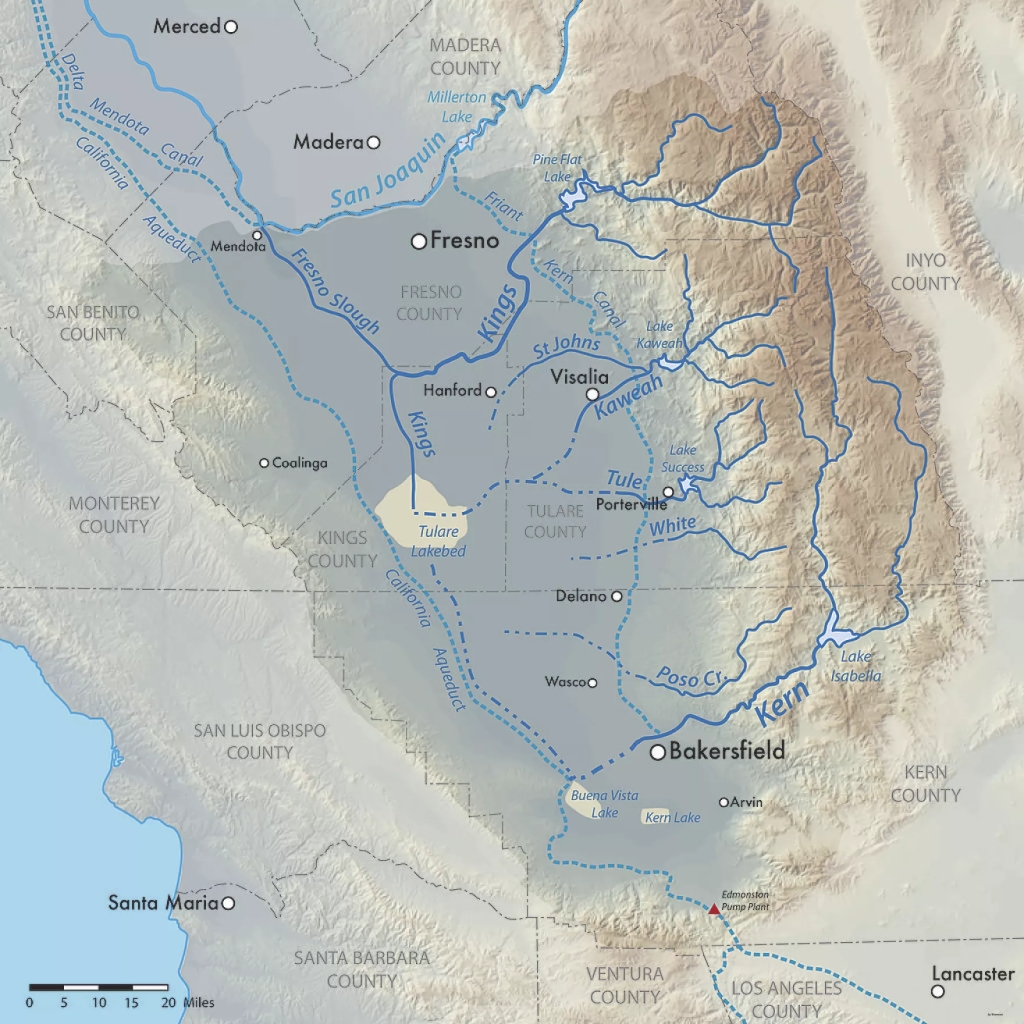
California and much of the wast have had far more precipitation than expected on the heels of years of drought. The existing canals and reservoirs in the watershed are overflowing and the dry lake bed with fields is getting flooded again; water doesn’t care about what is there now, it just flows downhill. Enter the 2023 version of Tulare Lake flooding farmland, roads, railways, towns, and other expensive infrastructure.
While it won’t return to its historic levels with one year’s snowpack, it’s likely that 100,000 acres (150 sq. miles) of farmland will be under water for two years, possibly more. This is a relatively lightly populated region, but some cities like Corcoran, CA (22,000 people) are on the edge of the old lake bed and might need to be partially evacuated as levees have failed to stem the tide.
Agricultural companies and local towns are both trying to protect their lands from flooding to protect their infrastructure, equipment, homes, and people. At times, these goals are at odds with one another, and armed guards are protecting levees and hydrologic projects. Below are two videos that are good introductions to the topic of the reemergence of Lake Tulare.
Questions to Ponder: How has agriculture and urbanization modified your state’s geography? What are the positive impacts of these modifications? What are potential negative consequences of these modifications?
TAGS: environmental modification, California, environment.

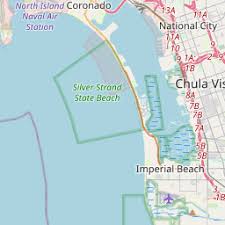
I was in the waves, enjoying the beach on my vacation to San Diego, when the importance of geographic scale to political governance hit me (I know, I’m a geography nerd…guilty). Local, state, national, and international organizations administer laws and regulations over space, and there are going to be overlapping jurisdictions and different priorities at different scales. I visited the two beaches I always went to as a kid, Coronado and Imperial Beach (IB). These are the two most southern beaches in California, and Coronado is now famous for the Top Gun: Maverick beach scenes with Point Loma in the background. Not surprisingly, tourism is incredibly important to these beach communities, especially in the summer. As is often the case, this little case study shows how geographic topics and scales are interlinked on the ground (or in the water as it were).

INTERNATIONAL CONTEXT: The Tijuana River flows through downtown Tijuana and crosses the U.S. border before emptying into the Pacific Ocean. The river is heavily industrialized in Mexico with pollutants and sewage from the major urban area of Tijuana, but the river is treated as a wetlands wilderness preserve in the once it crosses into the United States (downstream of the pollutants).
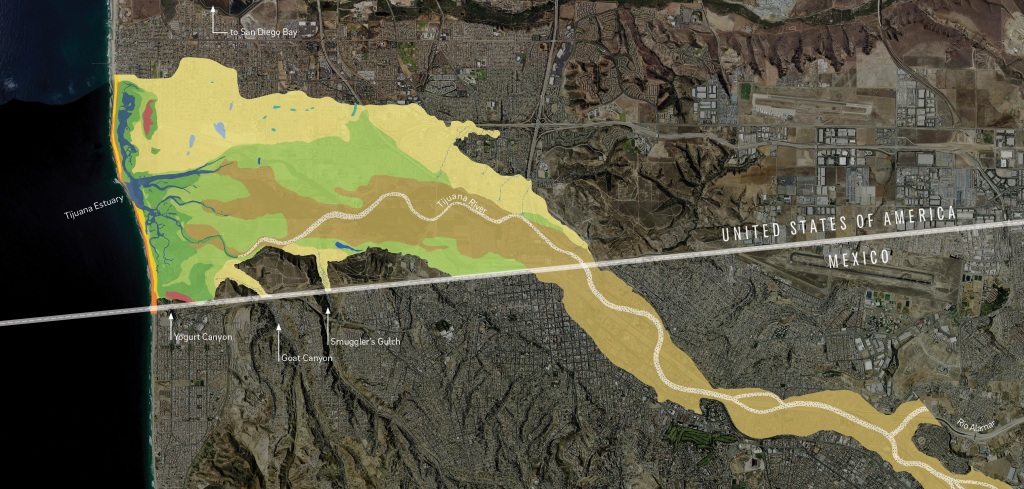
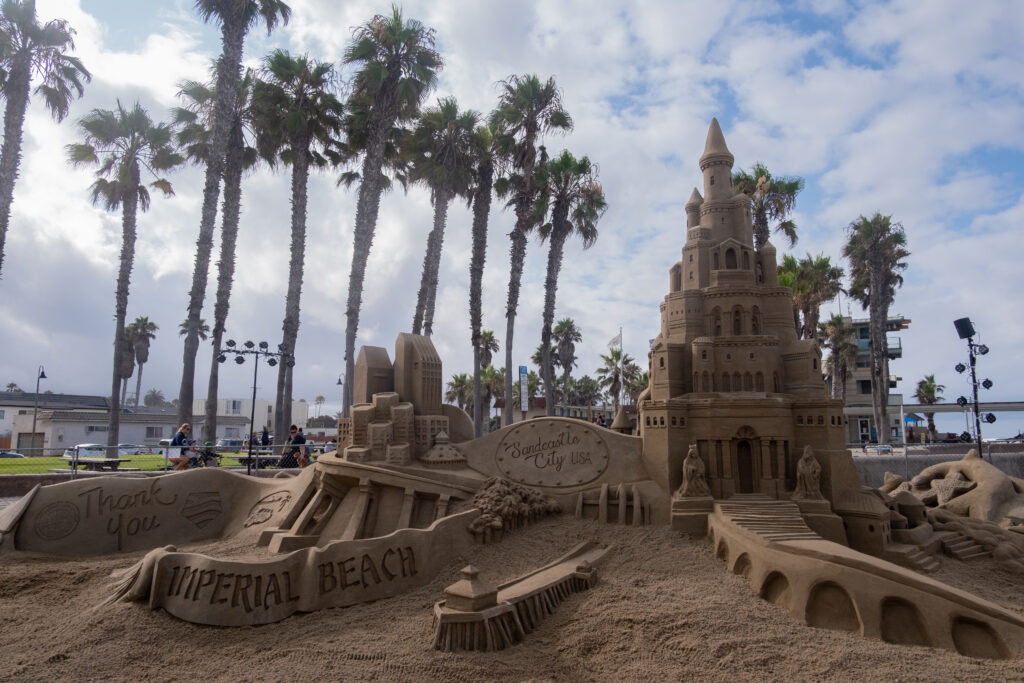
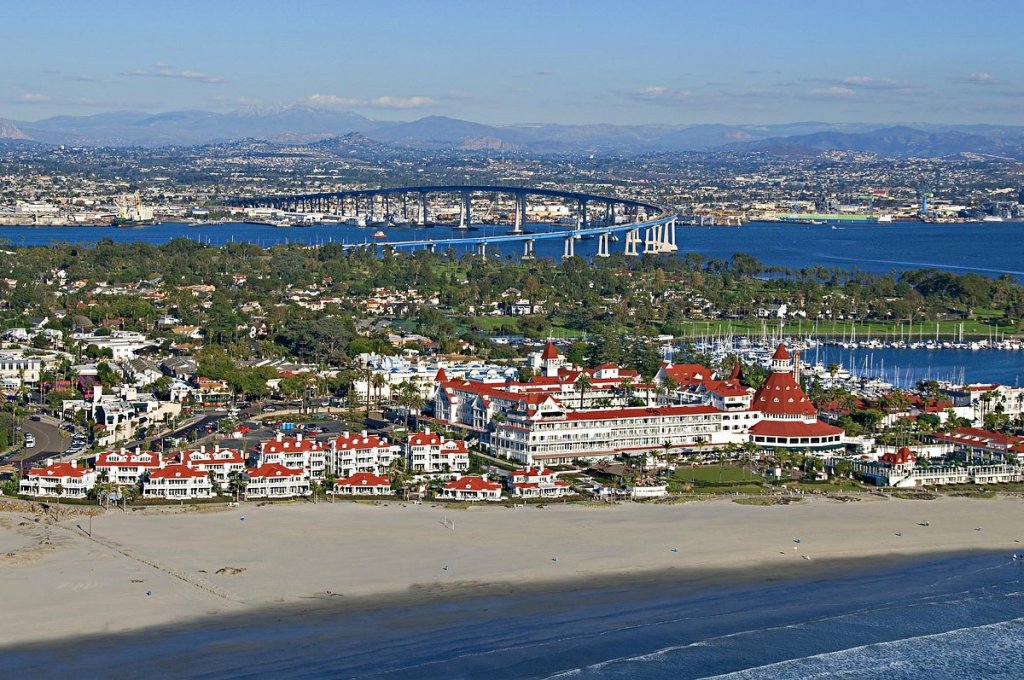
LOCAL (CITY) CONTEXT: The South Bay beach communities have built a summer economy around surfing, sandcastles, and chilling at the beach. This municipalities generate a substantial portion of local revenue from the shops, restaurants, and businesses (Hotel Del Coronado is the most famous seaside venue here).
COUNTY CONTEXT: In May, 2022, San Diego County changed their methods of testing water quality. They implemented a DNA test to screen for bacteria in the water. This test is more sensitive that the older tests and San Diego County is the only county in the U.S. using this heightened standard to measure water quality at the beach.
PANDEMIC CONTEXT: Public health is more on the forefront of people’s radar and many agencies are more risk averse than individuals.
SITUATION: The water at Imperial Beach, Silver Stand, and Coronado failed the new 2022 test more often than not even if it would have passed by the old standard. May and early June, the beaches were closed over 50% of the time. San Diego County cities can’t control the Tijuana River much before it crosses back into the United States, so they are limited on options to clean up the river, but the Federal government though, through the EPA, announced in 2021 that a $300 million initiative in conjunction with the Mexican government. This summer, Coronado has had to cancel large regional events and now the mayors, city councils, business leaders, and residents are pushing back against the new county testing procedures, citing economic damage to their communities. They have settled on a new advisory system that includes a comprise warning—one where the state is acknowledging that the water is polluted (3% chance of getting sick), but that people who have been to these beaches for years can choose for themselves to swim or not.
What is the right choice? Depends on your priorities (maintaining the tourist economy or public health benefits?) and the scale at which you are looking at the situation.
Tags: California, coastal, scale, environmental, political, pollution.


“As winter approaches each year, a haze of toxic smog envelopes vast swaths of northern India, including the capital New Delhi, forcing authorities to shut schools and restrict the use of private vehicles. Unlike southern parts of the country, most arid regions of northern India, including New Delhi, struggle with dust, a common air pollutant. Environmental experts say New Delhi’s topography hobbles efforts by authorities to stave off the spike in pollution. In recent years, the problem has been exacerbated by the burning of crop residues in Punjab and Haryana states, part of the farm belt that borders New Delhi. Relatively prosperous farmers from Punjab and Haryana, India’s grain bowl, have started using mechanised harvesters to gather the rice crop, partly to overcome the problem of rising labour costs.” SOURCE: Al Jazeera
Mexico City has a reputation for horrible air pollution–and rightfully so–but Delhi’s air pollution is worse and this year it is off the charts. Much of India faces air pollution problems, but northern India, and especially Delhi sees the convergence of urban, agricultural, demographic, and environmental factors to exacerbate the problems. Geographic problems are often intertwined and is a good issue to use a S.P.E.E.D. or E.S.P.N. activity.
GeoEd Tags: urban, agriculture, population, environment, pollution, South Asia, India.
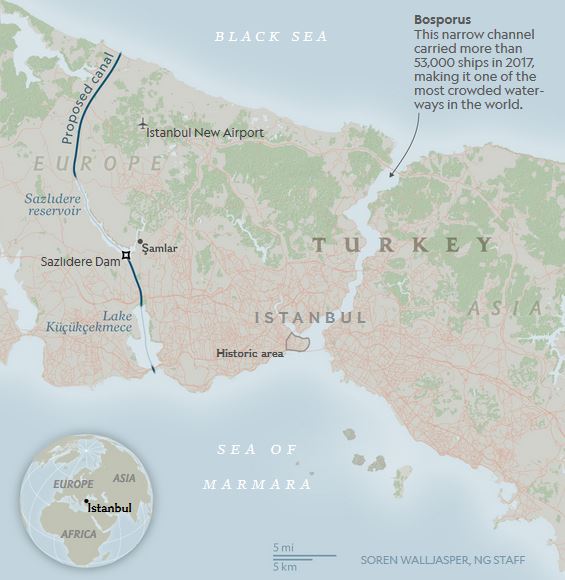
“The ambitious Canal Istanbul project could displace thousands of people, imperil the city’s tenuous water supply, and impact ocean life, critics say.”
Source: news.nationalgeographic.com
Istanbul’s location on the Bosporus has been vital to the Byzantine and Ottoman Empire as well as the modern state of Turkey. This is one of those crucial chokepoints of global commerce like the Straits of Malacca, and the demands on both of these natural waterways will soon exceed their capacity. Thailand is working on the Thai canal to relieve the pressures on the Straits of Malacca (and enrich themselves in the process); Nicaragua is also seeking to create an alternative to the Panama Canal which is in the process of expanding their locks to accommodate the massive container ships.
Istanbul is likewise looking to find other ways the keep their locational advantage as the gateway to the Black Sea region and beyond. Projects on this grand of a scale have tremendous real estate, trading, transportation and even tourism impacts. They can also bring negative impacts to the local water supply, wildlife, other environmental concerns. The bigger the project, the bigger the environmental risks and the greater the economic rewards.
GeoEd Tags: transportation, globalization, industry, economic, environment, political ecology, Turkey.
Scoop.it Tags: transportation, globalization, industry, economic, environment, political ecology, Turkey.
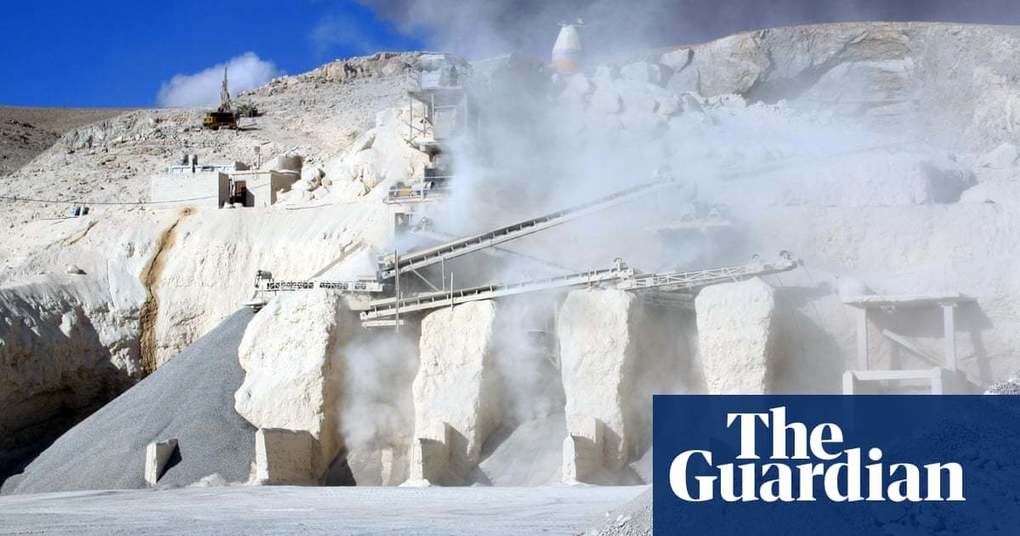
“After water, concrete is the most widely used substance on the planet. But its benefits mask enormous dangers to the planet, to human health – and to culture itself. Our blue and green world is becoming greyer by the second. If the cement industry were a country, it would be the third largest carbon dioxide emitter in the world with up to 2.8bn tonnes.”
GeoEd Tags: industry, sustainability, consumption, climate change, environment, architecture, resources.
Scoop.it Tags: industry, sustainability, consumption, climate change, environment, resources.
Source: www.theguardian.com
"The farther from the equator, the greater the seasonal swings."
Source: arstechnica.com
I’m not posting this in spite of its controversial nature—I am sharing this precisely because it raises eyebrows. Many have read this and see elements of environmental determinism while simultaneous recognizing some of its core assumptions. Arctic communities have devastatingly high suicide rates that most agree is in part impacted by the cold weather, the lack of sunshine, or in other words, the physical environment.
Questions to Ponder: How much environmental determinism actually is in this research and its assumptions? How much does latitude impact the human condition? How much of a factor is the environment in shaping cultural patterns? How would you adapt to the physical environment if you lived north of the the Arctic Circle?
GeoEd Tags: environment, music, Arctic, environment adapt, unit 1 geoprinciples.
Scoop.it Tags: environment, music, Arctic, environment adapt, unit 1 GeoPrinciples.
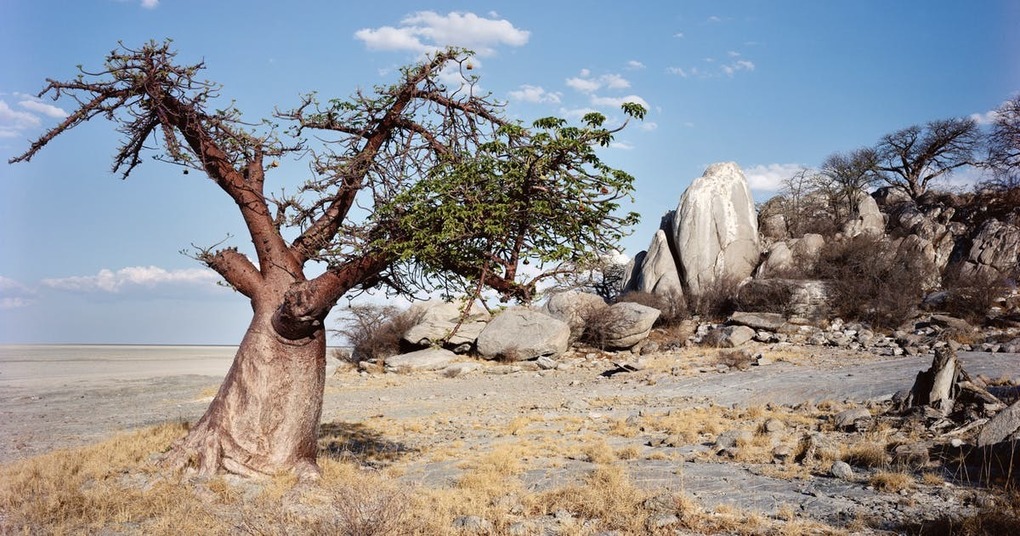
"Learn about one of the world’s most iconic tree species, the baobab tree, and discover why these endangered trees might be on their way to extinction—or might outlive us all."
Source: www.topic.com
So are the endangered baobab trees victims of the effects of climate change? The baobab, which has made so many wax poetic, is undergoing a steep decline. Although scientists are unsure of the reasons and possible solutions, this is a nice piece exploring the cultural and ecological significance of one of the more magnificent trees on our planet.
GeoEd Tags: biogeography, environment, ecology, Africa,political ecology, Botswana.
Scoop.it Tags: biogeography, environment, ecology, Africa, political ecology, Botswana.
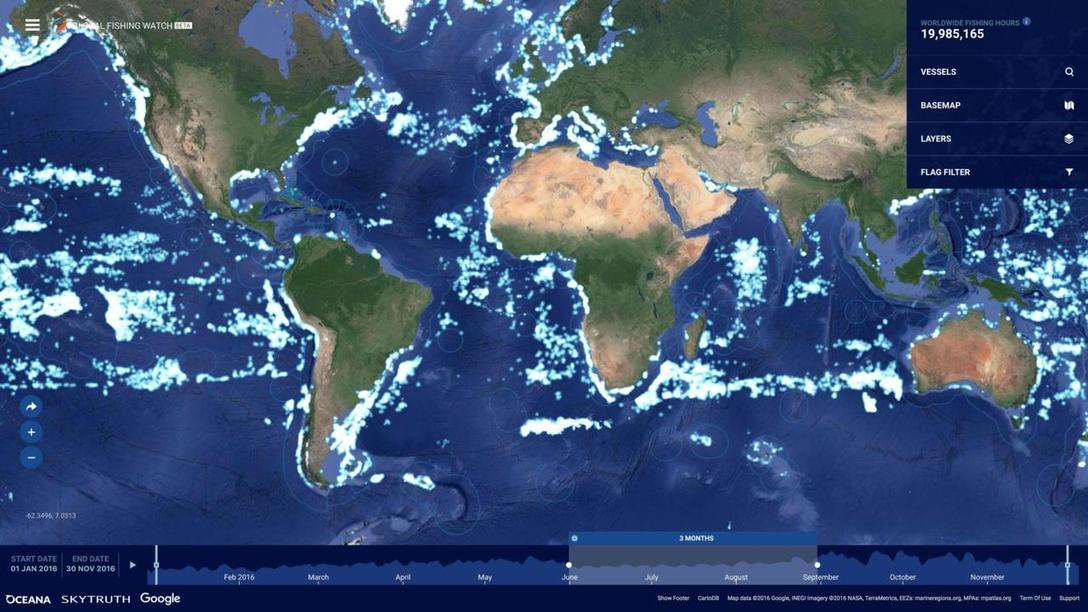
"The vast majority of fishing vessels follow the rules governing fishing – but many are not, and these bad actors can cause a lot of damage. Vessels may take too many fish – overfishing – which is causing our fisheries to collapse. Then there is the problem of illegal fishing, which can occur in protected areas, in another country’s waters or on the high seas. This threatens jobs and food security for millions of people, all around the world.
The trouble is, so much of this illegal activity is hidden – it happens out to sea, making it difficult to scrutinize what individual vessels are getting up to. Fortunately, we are now beginning to see what happens after commercial fishing vessels leave port.
The interactive map we created allows anyone in the world with an internet connection to see the activities of the commercial fishing fleet globally."
Scoop.it Tags: water, conservation, biogeography, environment, pollution, resources, mapping, food production, agriculture.
WordPress TAGS: water, biogeography, environment, pollution, resources, mapping, food production, agriculture.
Source: www.bbc.com