When the Dutch wanted to expand their territories, they turned to the North Sea to create more arable land for Dutch farmers. Likewise, Singapore has reclaimed land to expand their territories. Over 95% of Egypt’s population live along the Nile River and its fertile delta, and the population (over 110 million people) continues to grow and is seeking new options. While this isn’t expanding into the sea, it is a type of land reclamation project as they environment is modified to make the desert bloom. Both of these embedded videos are helpful introductions to the political, economic, demographic, and environmental aspects of these projects in the Middle East.
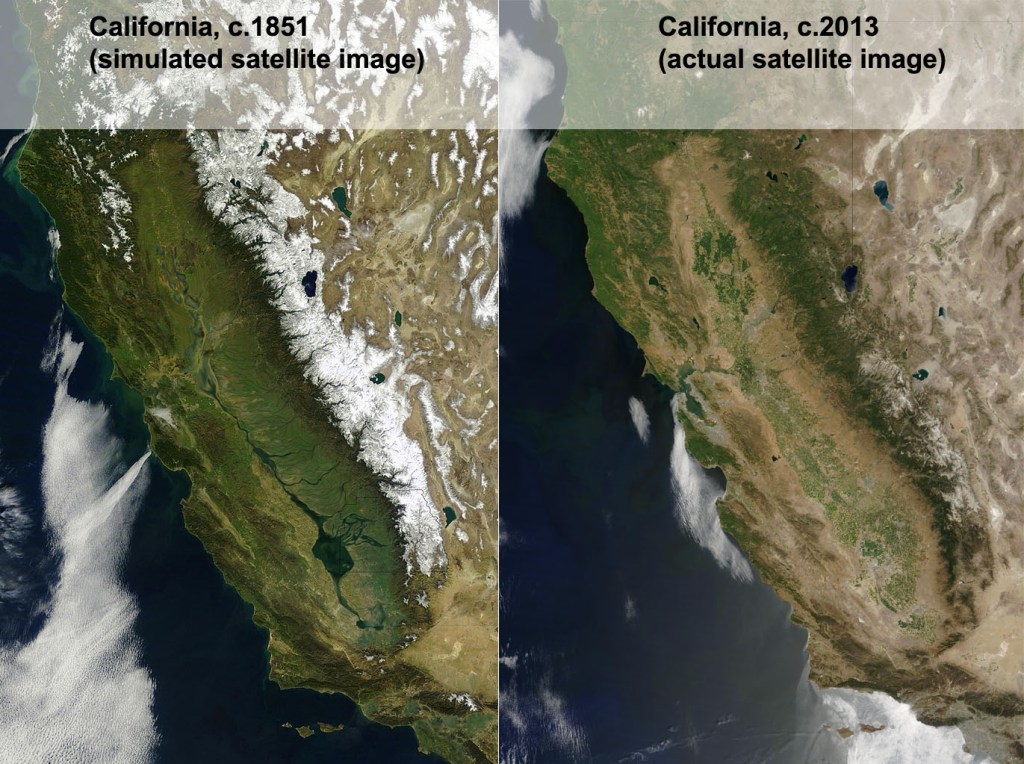
A few years ago, I was delighted to see an geographer’s rendition of what a satellite image of California would have looked if such a thing existed in the 1800s (figure 1). Back then the southern San Joaquin Valley was swampy wetland surrounding Lake Tulare, the largest freshwater lake west of the Mississippi River. In the late 1800s, canals and dams were created to divert water from the rivers that fed into the lake to go supporting agriculture and the metropolitan areas of California. As the very shallow lake dried up, the lakebed was converted into was converted to agricultural land, mainly under cotton cultivation.
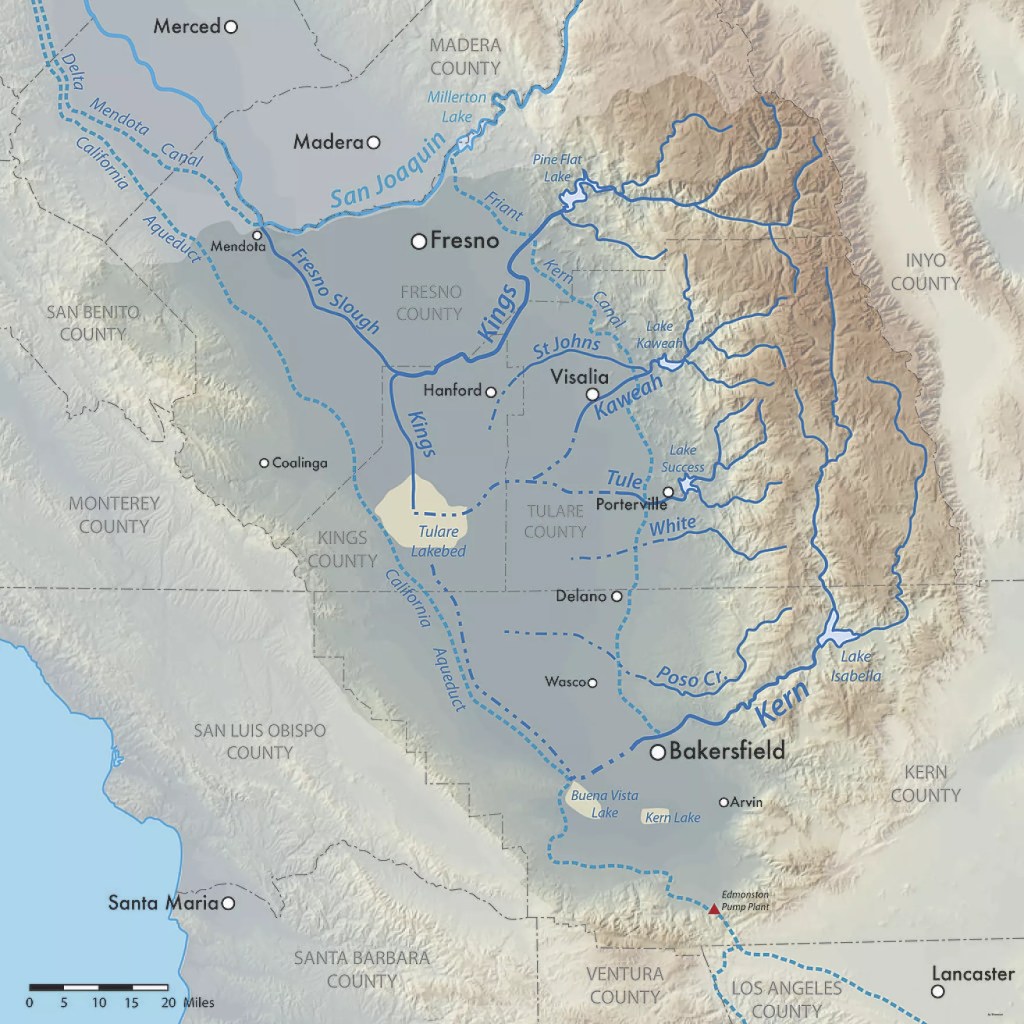
California and much of the wast have had far more precipitation than expected on the heels of years of drought. The existing canals and reservoirs in the watershed are overflowing and the dry lake bed with fields is getting flooded again; water doesn’t care about what is there now, it just flows downhill. Enter the 2023 version of Tulare Lake flooding farmland, roads, railways, towns, and other expensive infrastructure.
While it won’t return to its historic levels with one year’s snowpack, it’s likely that 100,000 acres (150 sq. miles) of farmland will be under water for two years, possibly more. This is a relatively lightly populated region, but some cities like Corcoran, CA (22,000 people) are on the edge of the old lake bed and might need to be partially evacuated as levees have failed to stem the tide.
Agricultural companies and local towns are both trying to protect their lands from flooding to protect their infrastructure, equipment, homes, and people. At times, these goals are at odds with one another, and armed guards are protecting levees and hydrologic projects. Below are two videos that are good introductions to the topic of the reemergence of Lake Tulare.
Questions to Ponder: How has agriculture and urbanization modified your state’s geography? What are the positive impacts of these modifications? What are potential negative consequences of these modifications?
TAGS: environmental modification, California, environment.
Lake Volta, the largest reservoir in the world, covers over 3% of the Ghana’s land. This video does a great job explaining the economic and political rationale that led the newly independent country of Ghana to sacrifice such a large portion of their territory (Super quick answer—to get electricity to fuel their economy and become the world’s leading aluminum producer). This hits on a variety of geographic themes: human and environmental interactions, modifications to the landscape, economic development, neocolonialism, migration through displacement, globalization, etc.
Tags: Africa, development, Ghana.

I’d like to interject two geographic terms/concepts not mentioned in the video below about New Orleans: site and situation. I would argue that in New Orleans has a horrible site (the features of a given location) but a very attractive situation (the connection and relationship to other places and resources). The first 4.5 minutes of this video nicely highlights the contrast of an incredible situation on a horrible site; this would be a great clip for a general audience (human geography or regional geography). The remaining portion of the video is still good, but more narrowly focused on the increasingly negative environmental context of New Orleans’ urban ecology.
Geographers make a distinction between site and situation as they consider the underlying foundation of a place. Few cities represent such a wide chasm between these two aspects as does New Orleans. The situation, or the answer to why does a place exist, was imperative. The Mississippi River was a major artery for the North American continent. As first the Europeans and then the Americans assumed control of the area, a port was essential at the mouth of this river. But the site, the response to where a city is placed, continues to confound. Few environments were or are more inhospitable to human habitation. Poor soil, disease, floods, and hurricanes are constant threats that have plagued the city for over three centuries. But the why trumped the where and hence the paradox of New Orleans persists.
TAGS: Urban ecology, human and environmental modifications.
Cape Town is running out of water. Israel offers some lessons on how to avoid that fate.
Source: foreignpolicy.com
Most droughts are caused by a combination of human and physical geographic factors. Cape Town is current in the midst of a 3 year long drought that is causing many officials to consider drastic measures such as cutting off all private water taps and rationing out 13 gallons per resident per day.
I would like for us to also consider cases beyond South Africa, and think about the the broader issues of resource management, urbanization, resilience, and changing climatic conditions. Resources Watch discusses critical water shortages in Morocco, India, Iraq and Spain with excellent maps, charts, and graphs. This article from Foreign Policy demonstrates how Israel has worked to maximize their minimal water resources (recycling grey water for agriculture and desalinization). The World Resources Institute discusses 3 things cities can glean from the South African crisis (1. Understand risks, 2. Manage the water budget, and 3. Invest in resilience).
Tags: drought, water, environment, technology, environment modify, South Africa, Israel, Spain, Morocco, India, Iraq.
A costly plan to build floating islands shows how climate change is pushing the search for innovative solutions, but some critics ask who will ultimately benefit.
Source: www.nytimes.com
As coastal communities are considering what the tangible impacts of climate change might be, things that were once considered science fiction could be a part of how people adapt to the modifications we’ve collectively made to our global environment that we depend on to sustain life.
Tags: physical, technology, sustainability, climate change, environment, resources, water, coastal, environment depend, environment adapt, environment modify.
“Watch salmon race across the road on their way to spawn; for more footage, watch this extended version.”
Source: www.youtube.com
We often see examples of how human modifications to ecosystems or watersheds have devastatingly negative impacts. This is a remarkable example from Washington’s Olympic Peninsula that shows the resiliency of natural systems to overcome human modifications to the physical landscape. If you study the world, you will always have something to both amaze and surprise you.
Tags: fluvial, biogeography, environment, geomorphology, physical, water, environment adapt, environment modify.
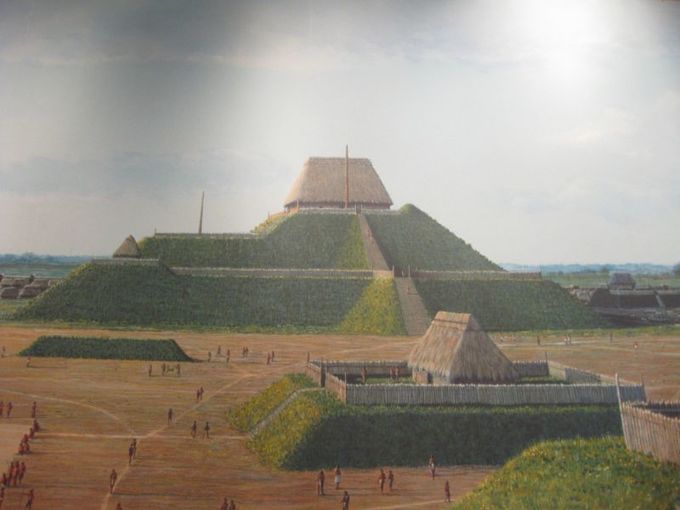
Cahokia was North America’s biggest city—then it was completely abandoned. I went there to find out why.
Source: arstechnica.com
The earthen mounds of Cahokia on the flat flood plains must have been the most awe-inspiring demonstration of political power and economic wealth in its day. Like so many other civilizations before them (and many more in the future?), Cahokia probably declined from too many environmental modifications that led to unforeseen consequences.
Tags: urban ecology, indigenous, environment, environment modify, historical, North America.
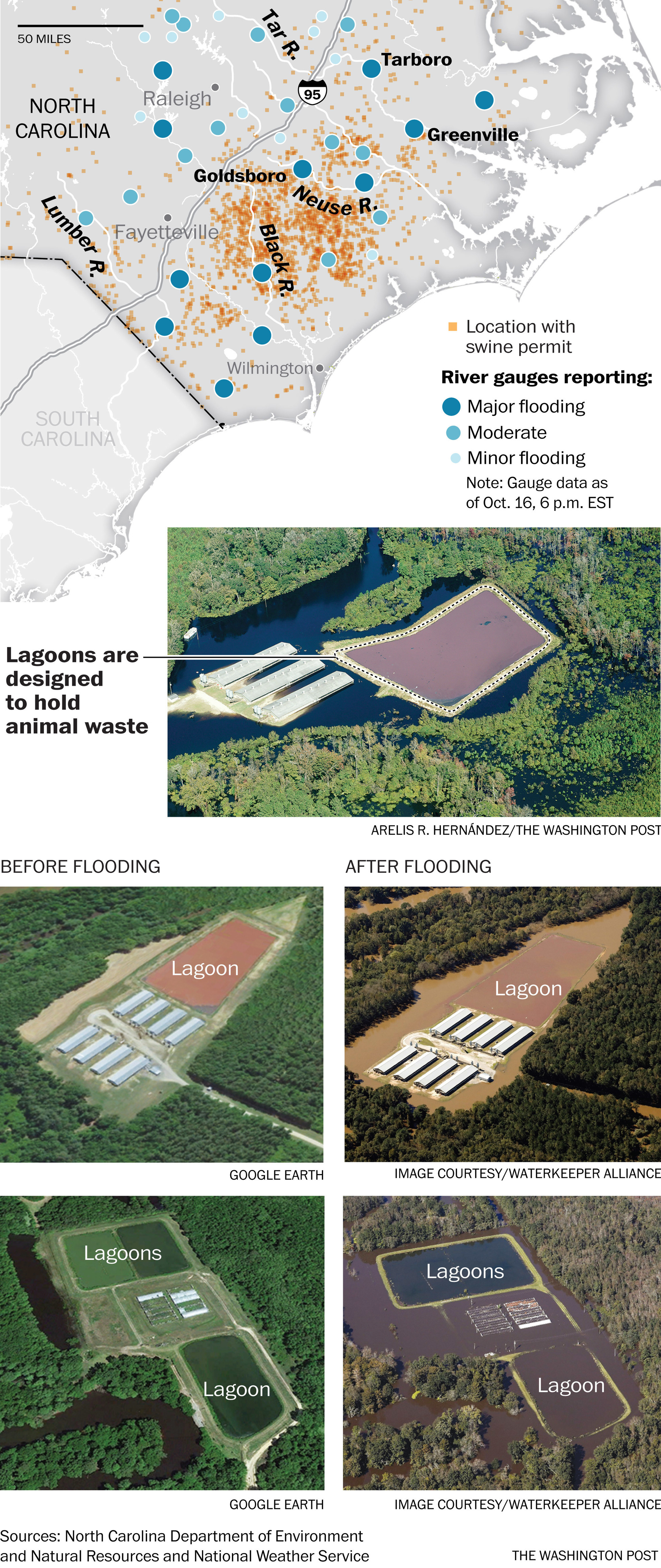
As fecal waste and bacteria flow from hog lagoons into the water supply, North Carolina is revisiting a contentious battle between the pork industry, health experts and environmentalists.
In regions where hog farm density is high, there is an overall poor sanitary quality of surface waters. The presence of mass-scale swine and poultry lots and processing plants in a sandy floodplain – a region once dotted by small tobacco farms – has long posed a difficult dilemma for a state where swine and poultry represent billions of dollars a year for the economy. [Past] hurricane’s environmental impact in North Carolina were so severe in part because of the large number of hog lagoon breaches. Following Hurricane Matthew, the department has counted 10 to 12 lagoons that were inundated, with floodwaters topping the berms and spreading diluted waste.
Tags: food, agriculture, agribusiness, unit 5 agriculture, agricultural environment, environment, environment modify, pollution.
Source: www.washingtonpost.com